Reducing the occurrence of false alarms is important to home alarm security systems; otherwise, people may feel frustrated and get discouraged from investing in such systems. PIR sensors, an essential component in home security systems, play a vital role in detecting suspicious human movements and activating alarms accordingly.
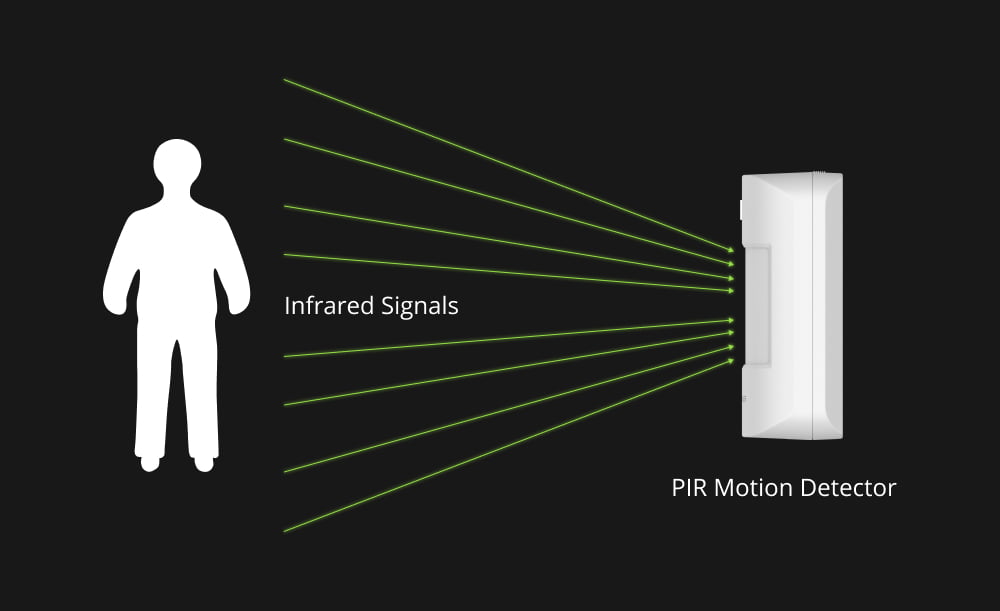
However, these sensors are susceptible to environmental temperature fluctuations, as they work by measuring IR changes emitted by objects, humans, and pets with varying temperatures. But you may wonder: How can one enhance PIR sensor detection precision to mitigate this challenge? Keep reading to find out!
What is Digital Temperature Compensation Technology?
Digital temperature compensation is a method used to correct temperature errors in the PIR sensor’s output signal. PIR sensors use digital temperature compensation technology to remain effective and accurate within the entire permissible temperature range of the device.
Under ideal conditions, the human body temperature, which is typically around 36.6°C, differs from the ambient temperature. This temperature difference is what allows the PIR detector to accurately detect the movement of a person in space.
However, there are instances, such as in summer climate or some countries & regions, where the two temperatures can be very close. In such a situation, temperature compensation is necessary.
A PIR sensor with digital temperature compensation technology measures the ambient temperature using a temperature compensation sensor. It then performs real-time temperature compensation on the sensor output through a digital processing algorithm to continuously monitor and correct temperature errors, improving the accuracy and stability of the measurement.
For example, with each ambient temperature measurement, usually ranging from 14°C to 42°C, the sensor introduces a correction according to the table of correction factors stored in its memory, either decreasing or increasing the sensitivity of PIR sensors.
This enables PIR sensors with digital temperature compensation to provide more accurate and reliable measurement results, especially in applications where there are wide temperature ranges and large temperature fluctuations.
How Does Digital Temperature Compensation Work on PIR Motion Sensors Exactly?
Passive infrared detectors mainly track the infrared radiation signals of moving human bodies and filter out interference from nature and false signals caused by animals. The sensors usually utilize pyroelectric elements to detect infrared radiation.
When a human being enters the PIR sensor’s detection area, the temperature difference between the ambient environment and the human body causes the pyroelectric element to experience a change in infrared radiation temperature.
Read More: What is PIR Sensor and How Does It Work?
This causes the charge balance within the pyroelectric element to be upset, causing the release of charges. The released charges are then detected and processed by the passive infrared detector as temperature-related errors in the signal output.
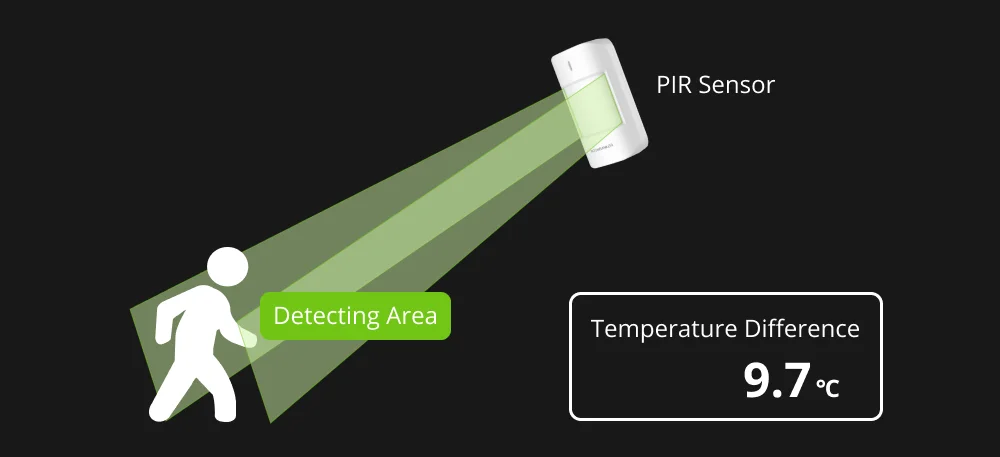
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the detection results, and to improve detection errors caused by temperature, PIR motion sensors with sensitivity adjustment are incorporated with digital temperature compensation technology. This allows them to automatically adjust the alarm threshold based on external temperature changes.
Also Read: What Is PIR Motion Sensitivity and Can It be Automatically Adjusted?
NOTE: The technical working principle can be mainly divided into five steps, as discussed in the below section:
Five steps of the technical working principle of digital temperature compensation on PIR motion sensors
The technical working principle can be mainly divided into the following steps:
Step 1: Temperature measurement:
The PIR motion detectors with built-in temperature sensors, such as NTC thermistors, measure the ambient temperature. This sensor is usually called a temperature compensation sensor.
Step 2: Sensor output collection
At different temperatures, temperature compensation sensors (NTC thermistor) will show different resistance characteristics, as shown in the figure below.
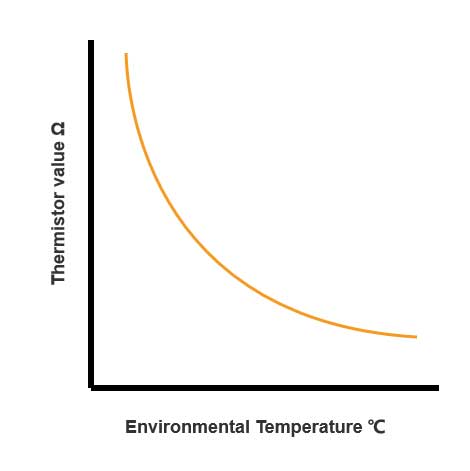
This converts the temperature information into electrical signals and transmits them to digital processing circuits.
Step 3: Digital processing
The digital processing circuit receives the signal from the sensor and processes the signal using a built-in temperature compensation algorithm or calibration model. These algorithms can calculate temperature errors based on predetermined temperature characteristics curves or models of different materials.
Step 4: Temperature compensation calculation
Based on the processed temperature signal and calibration model, the digital processing circuit calculates the temperature compensation value. This compensation value represents the error in the sensor output data due to temperature changes.
Step 5: Output correction
Temperature compensation value is applied to the output signal of the sensor to correct the measurement results or other related parameters affected by temperature. This can eliminate the impact of temperature changes on system performance and improve the accuracy and stability of PIR detector measurements.

Using Roombanker’s PIR Motion Sensor Help Your Home Security Businesses
Roombanker’s PIR Motion Sensor is a game-changer for PIR Alarm System, offering a host of features designed to eliminate the impact of temperature changes and enhance protection.
Here are some of the reasons why you should consider using Roombanker’s PIR Motion Sensor:
- Advanced detection technologies: Roombanker’s sensor is equipped with sophisticated detection technologies, including Anti-White Light and Independent Floating Threshold technology, and digital temperature compensation to optimize PIR sensor performance. By filtering out false alarms triggered by natural phenomena or artificial lighting and compensating for temperature variation, this sensor ensures the output of accurate detection results in different environments.
- Ultra-long distance wireless data transmission: Roombanker’s PIR sensor utilizes the innovative RBF protocol for seamless two-way encrypted communication with the Home Security Hub, which boasts a transmission range of 3100 meters in open space. This ultra long wireless sensor-to-hub communication range makes it suitable for a variety of scenarios, from small residential properties to expansive commercial spaces.
- Pet-immune PIR security: Roombanker’s PIR sensor adopts the anti-pet design. Pets weighing below 10kg will not activate the alarm. By differentiating between human intruders and household pets, the pet-immune PIR sensor minimizes false alarms, ensuring that security alerts are triggered only by genuine threats.
Also Read: What is Pet-friendly PIR Sensor and Why It Is Essential to Home Security Solutions?
Roombanker Wireless Security Alarm System combines ease of use with professional-grade features, offering effortless DIY installation and set up while integrating professional-grade features, including advanced detectors, a dedicated security hub, and supporting integration with Alarm Receiving Centres, etc, making it the go-to choice for a reliable wireless security alarm system, supporting intrusion alarm, fire & water leak alarm, panic alarm, etc., serving an array of small business and residential properties.
